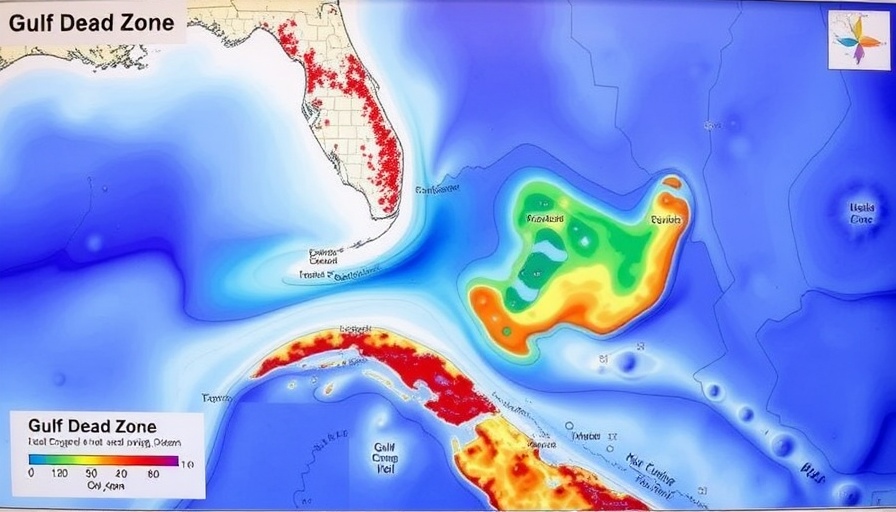
The Growing Concern of the Gulf's 'Dead Zone'
This summer, environmental scientists expect the Gulf of Mexico's 'dead zone' to expand significantly, covering approximately 5,574 square miles. This alarming forecast underscores the critical need for attention to pollution management in the Mississippi-Atchafalaya watershed. To put this into perspective, the dead zone is projected to be about three times the size of Delaware, devastating wildlife habitats and disrupting local economies dependent on marine life.
Understanding Dead Zones: What They Mean for Marine Life
Dead zones occur when levels of oxygen in water drop so low that marine life cannot survive. This hypoxia is largely caused by nutrient runoff from agricultural activities, wastewater discharge, and urban development. As nutrient pollution saturates the waters, algae blooms proliferate, consuming oxygen and rendering the water inhospitable for fish and other aquatic organisms. Such conditions threaten the biodiversity vital for a balanced ecosystem.
Implications for Local Economies and Fisheries
The ramifications of a large dead zone extend beyond ecology; they directly impact the economy. With diminishing fish populations and uninhabitable waters, fishing industries are expected to suffer, leading to reduced catches and possible job losses. Coastal tourism also faces challenges, as less thriving marine life may deter visitors seeking recreational fishing and water activities.
Insights from Experts: The Call for Immediate Action
Experts contend that comprehensive action is necessary to mitigate this annual occurrence. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) emphasizes the urgency of curbing nutrient runoff. Implementing best management practices in agriculture and enhancing wastewater treatment could significantly decrease pollution levels in the watershed, thereby diminishing the size and frequency of the dead zone.
Looking Ahead: The Future of the Gulf Ecosystem
The potential for remedial measures remains—if local governments, industries, and communities collaborate effectively. Awareness campaigns aimed at educating farmers and the public about nutrient management could foster a sustainable approach to protecting the Gulf. Continued research into innovative farming practices and their effects on water quality will be crucial in the years to come. While the current forecast is concerning, proactive solutions can pave the way for a healthier marine environment.
As the summer approaches and marine life braces for impact, it’s vital for stakeholders at every level to engage in conversations around water quality and ecological preservation. The health of the Gulf—and its economic contributors—depends on it.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment